
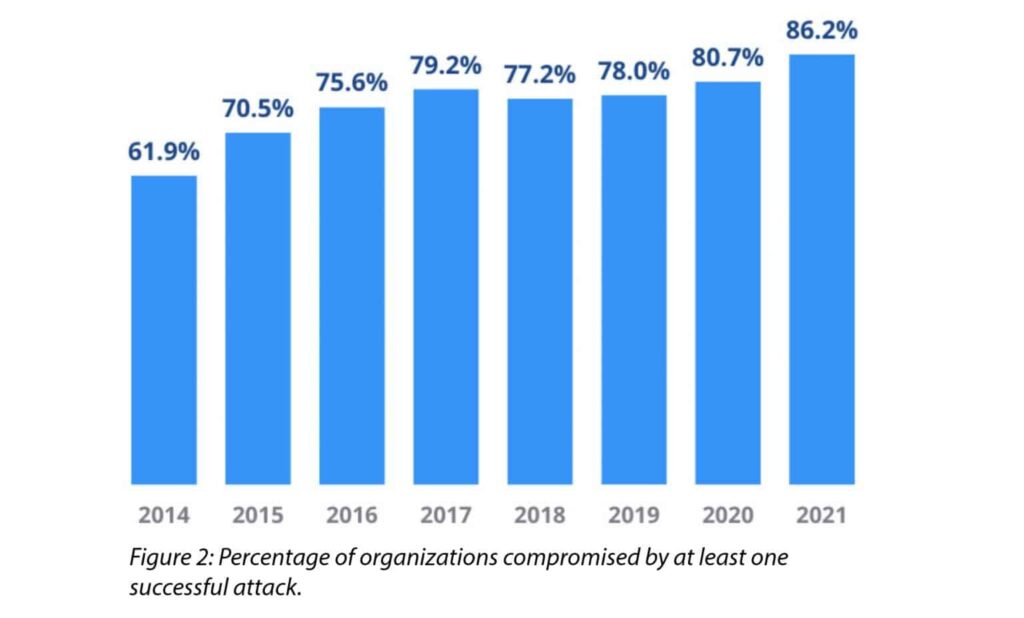
Every year it is evident that the number of cyber crime complaint reported across India increases at a rapid rate.
The nature of the crimes, in contrast, ranged from petty online frauds to sexual harassment and lottery scams.
The area most targeted, however, is the financial and banking segment. Since the onset of the coronavirus outbreak and most of the services moving to the internet, the risk of being more vulnerable extends to other sectors too.
Although the private sector bears the brunt of the crime online and in the public sector, government agencies have faced data breaches.
The internet, mobile phones, and computers have revolutionized modern life, offering many benefits.
Information technology can make us more vulnerable to many threats. These threats can cause financial loss and damage to our reputation.
Cybercriminals can easily gain access to your digital life if you make a small error. Hacking is becoming more common, and cybercrime in India is rising.
Cyberstalking, morphing, and online harassment are the most common types of cybercrimes against females.
Therefore, crucial to learn how to avoid cybercrimes. When and how to report cyber crimes and what preventive steps you can take to stop them.

What is Cybercrime?
Cybercrimes can be described as wrongful acts or crimes committed using technology.
Cybercrime is a crime that involves the use of technology as the primary tool of crime. However, there is no clear definition.
Nearly all states have cyber cell departments available to address cyber-related issues in India.
Background
Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India, has set up ‘Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centr (I4C)’ to deal with cybercrimes in a coordinated and comprehensive manner. Following are seven
components of the centre:
- National Cybercrime Threat Analytics Unit (TAU)
- National Cybercrime Forensic Laboratory (NCFL)
- National Cybercrime Training Centre (NCTC)
- Cybercrime Ecosystem Management
- A platform for Joint Cybercrime Investigation Team
- National Cybercrime Reporting Portal
- National Cyber Research and Innovation Centre (NCR&IC)
One of the components of I4C is operationalisation of the National Cybercrime Reporting Portal to deal with all types of cybercrimes.
The earlier Cybercrime Reporting Portal www.cybercrime.gov.in was for filing cybercrime complaints pertaining to Child Pornography (CP)/ Rape, Gang Rape (RGR)/ Obscene Content only.
However, the National Cybercrime Reporting Portal facilitates the filing of all cybercrimes with a particular focus on cybercrime against women and children.
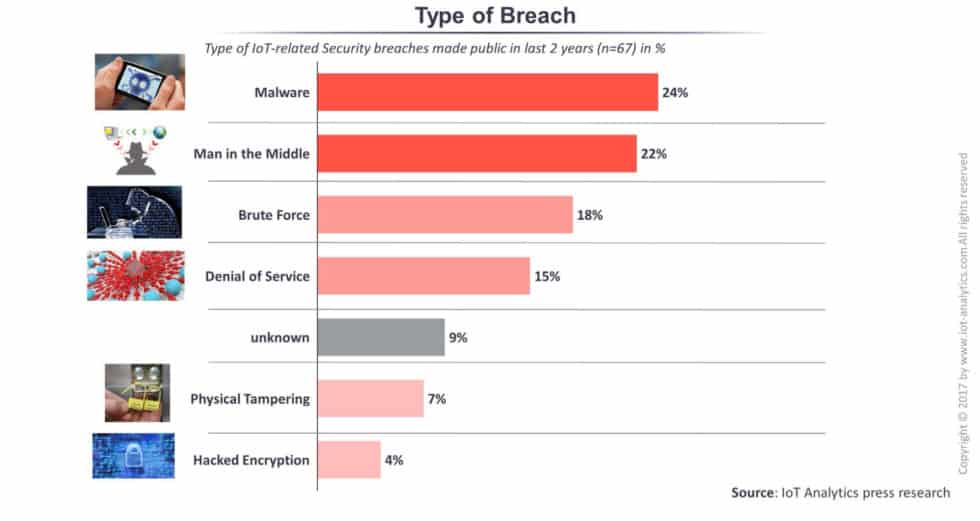
Certain Types of Cyber Crimes in India:
Many types of cybercrimes have been identified according to the Cyber Law in India, such as
- Phishing – An individual or group of malicious people who attempt to scam users. They send e-mails to victims or create web pages designed to collect their login information. Sections 66 C,66 D, and Section 74 of the IT Act provide prosecution for anyone suspected of phishing. Penalties can be up to three years or a fine of up to one lakh rupees.
- Credit Card Fraud – Card fraud can be defined as theft or manipulation of account data. Section 66 C, 66 D, and sections 468 & 471 of IPC, respectively, provide fraud provisions.
- Online theft – When a criminal extorts money from their victim, you can access the victim’s bank account data, credit card, and debit card details, as well as other sensitive information, over the internet. Section 66 C Imprisonment of either description up to 3 years and/or fine up to Rs. 1 lakh.
- Denial Of Service – It shuts down any server. It’s also known as the flooding engine, which sends requests to overload systems. It also uses bots to perform tasks. These provisions are found under section 43(f), IT Act. They can lead to imprisonment of up to 3 years and/or a fine of up to 5 lakh rupees.
- Virus Dissemination – This involves unauthorized or direct access to the system through search or by searching for malicious programs such as viruses, trojans, etc. Worms can be standalone or require a host. The IT Act, 2000, sections 43-C, 66, and 268 of the Indian Penal Code, provides the provisions.
- Hacking – Hacking is when someone hacks into another person’s computer to gain access to their sensitive and personal information, such as bank details, email accounts, etc. Hacking is becoming more common as everything becomes digital.
- Cyberstalking – is the most common type of cybercrime cell complaint or online cybercrime complaints. Cyberstalking is a crime that involves online harassment, usually against women. It’s similar to offline stalking but online.
- Cyberbullying – When the internet, mobiles, or social networks can be used to harass, intimidate, or defame a person.
- Child abuse and solicitation – When children are contacted via the internet to make child pornography.
- Cyber Terrorism – When a person is threatened with extortion or any other crime, it is cyber terrorism.
How to file Cyber Crime Complaint
Most Indian cities have a cyber crime cell. Online or offline, you can file a complaint to the cyber police.
The IT Act states that cyber crimes fall under global jurisdiction.
This means that cyber crime complaints can be filed with any cyber cell in India regardless of where they were committed or where the victim is located/residing.
To punish cyber criminals, the first and foremost step is to file complaints.
A written complaint must be filed with any cyber crime cell in the jurisdiction, and you will need to include your name, contact information, and address for mailing in the written complaint.
The written complaint should be addressed to the Head Cyber Crime Cell in the city you are filing the cybercrime complaint.
You can file a First Information Report at your local police station if you don’t have access to any cyber cells in India.
If your complaint is not received there, you can contact the Commissioner or the Judicial Magistrate of the city.
The IPC covers certain cybercrime offenses. You can file an FIR for cybercrime at your nearest police station to report cyber crimes.
It is mandatory under Section 154 of CrPC for every police officer to record the information/complaint of an offense, irrespective of the jurisdiction in which the crime was committed.
How do I file a Cyber Crime Complaint online?
The online portal where a victim can file a cyber crime complaint is https://cybercrime.gov.in/
An initiative of the Government of India that caters to complaints pertaining to the online Child Pornography (CP), Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM), or sexually explicit content such as Rape/Gang Rape (CP/RGR) content and other cybercrimes such as social media crimes, online financial frauds, ransomware, hacking, cryptocurrency crimes, and online cyber trafficking.
You can also report anonymously Child Pornography (CP), or sexually explicit content (RGR), through the portal.

To report a cybercrime online, you can follow the steps below.
Step 1:
Step 2:
Click on “Report Other Cyber Crimes” on the menu.
Step 3:
Click on “File a complaint”
Step 4:
Please read the conditions and agree to them.
Step 5:
Register your cell phone number, OTP and enter your name and state.
Step 6:
Enter the details of the offense.
Note:
Anonymous reporting is also possible.
Cyber Crime Complaint Number and Address of Cyber Cell
Cyber-Crime-Cell


0 Comments